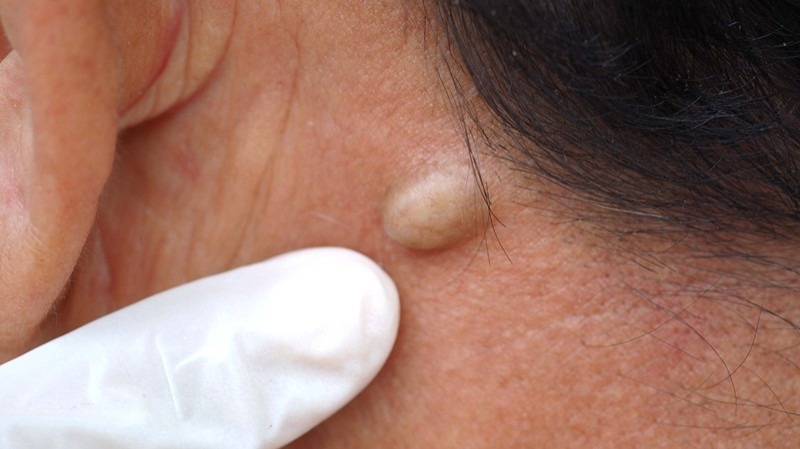
A cyst is a small, sac-like pocket of tissue that is often filled with fluid, air, or other substances. These growths can occur in various parts of the body or under the skin. While most cysts are benign (non-cancerous), some may require treatment due to complications such as pain, infection, or inflammation.
What is a Cyst?
Cysts are formed when the body’s natural process of cell growth or waste removal is disrupted. They can form in organs, on the skin, or even in soft tissues. In some cases, cysts can be caused by an injury, infection, or blockage in the body’s ducts. Most of the time, cysts do not cause harm, but their size and location may make them uncomfortable or cause other health issues. The necessity for treatment largely depends on factors such as the type, size, and location of the cyst, as well as whether it is infected or causing discomfort.
Types of Cysts and How They Appear
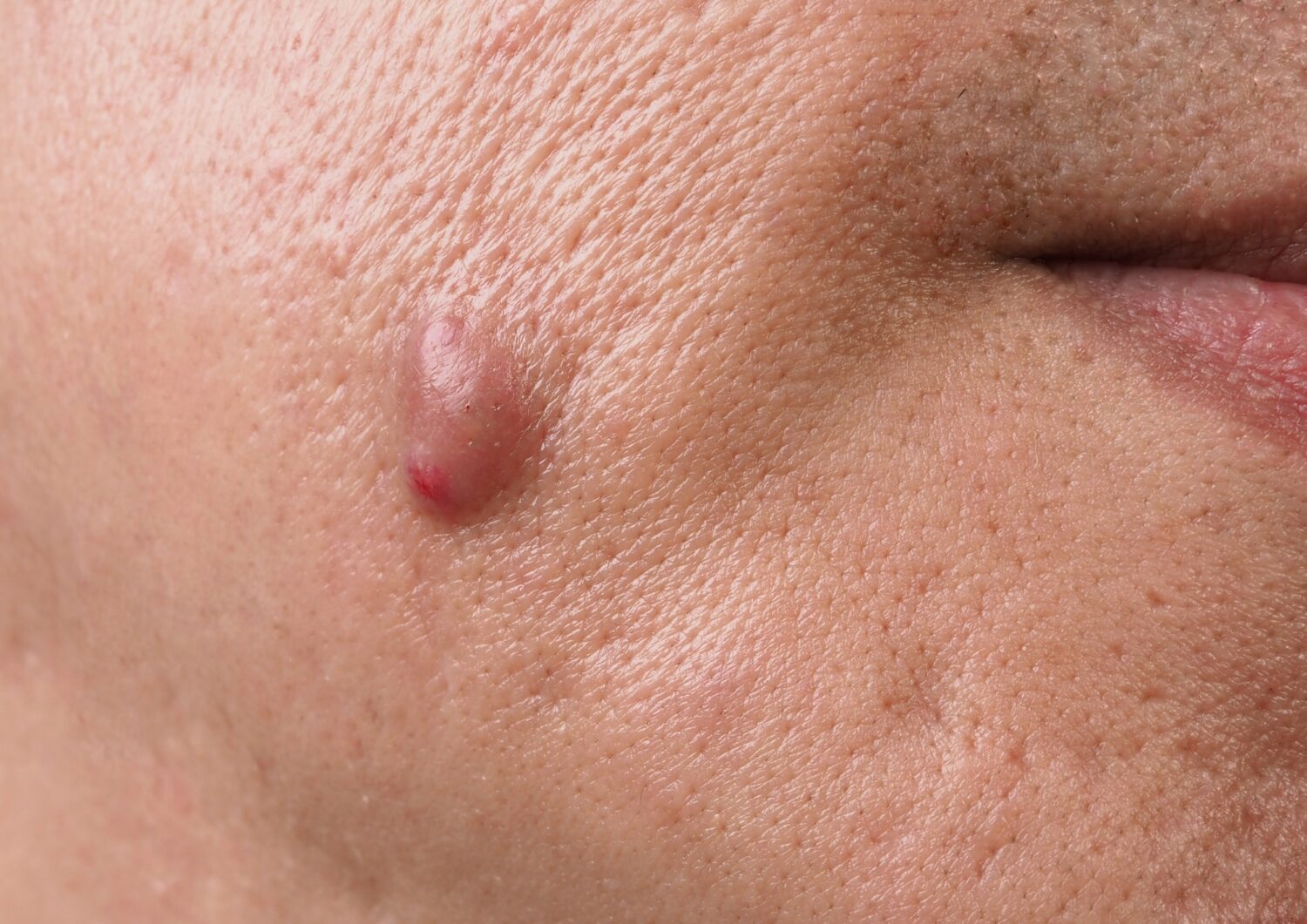
There are several different types of cysts that can appear on or inside the body. Each type has its own characteristics and potential causes. Below are some common types of cysts, including descriptions and visual representations:
1. Epidermoid Cyst
Epidermoid cysts are filled with keratin, a protein found in the skin, hair, and nails. They usually occur when a hair follicle becomes blocked, causing skin cells to collect beneath the surface. These cysts often appear as small, skin-colored, tan, or yellowish bumps. They typically form on the face, neck, or torso but can develop anywhere on the body.
2. Sebaceous Cyst
Sebaceous cysts form in sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing oil to lubricate the skin and hair. These cysts are often filled with sebum (oil) and are commonly found on the face, neck, or torso. Sebaceous cysts are often the result of damage to the sebaceous glands.
3. Breast Cyst
Breast cysts are non-cancerous fluid-filled sacs that develop in the breast tissue. While most breast cysts are benign, they can cause tenderness or discomfort in the affected area. Regular breast self-exams and routine check-ups are important to monitor any changes in the breast tissue.
4. Ganglion Cyst
A ganglion cyst is a fluid-filled lump that usually appears near joints, particularly in the hands, wrists, ankles, and feet. Ganglion cysts can develop due to repetitive movements, joint injuries, or other stress-related factors. While they are often harmless, they can cause pain or limited range of motion if they press against surrounding tissues.
5. Pilonidal Cyst
Pilonidal cysts are typically found at the top of the buttocks. They are often caused by hair growth, friction from sitting, or hormonal changes. These cysts may become infected and cause pain, swelling, or drainage of pus. Pilonidal cysts are more common in young adults and can require surgical intervention if they become recurrent or infected.
6. Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries. These cysts can develop when an egg-producing follicle fails to open or when it re-closes and collects fluid. Ovarian cysts are most common in women of reproductive age and are typically discovered during routine pelvic exams. In some cases, ovarian cysts may cause pain or discomfort, and if left untreated, they can lead to complications.
7. Baker’s Cyst
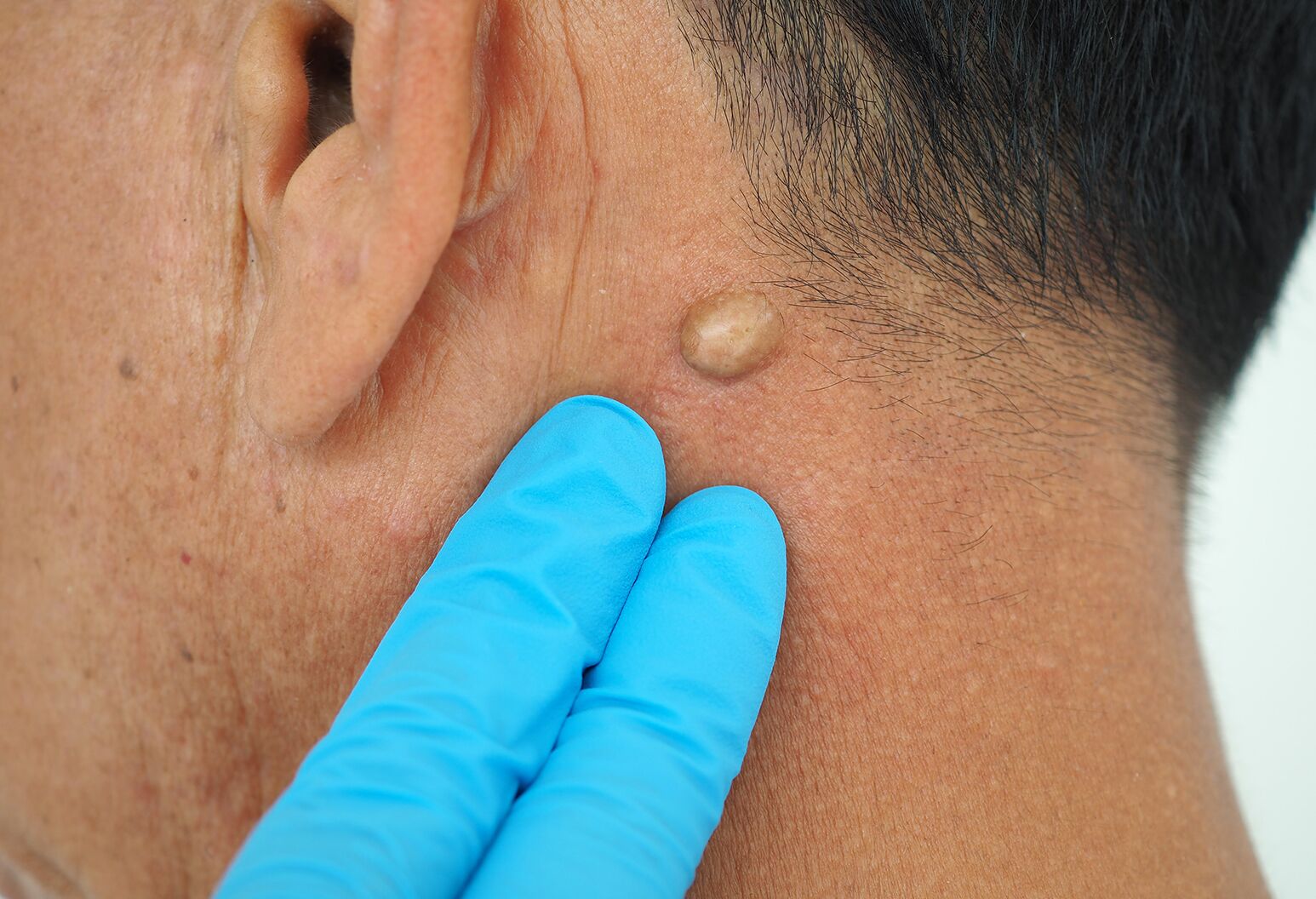
A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled sac located at the back of the knee. It can develop due to arthritis, inflammation, or injury to the knee joint. Baker’s cysts often cause swelling and discomfort in the knee and may restrict movement. Treatment may include physical therapy, fluid drainage, or medication.
8. Pilar Cyst
Pilar cysts are non-cancerous, skin-colored bumps that often form on the scalp. They are typically filled with keratin, the same substance found in epidermoid cysts. While these cysts are not cancerous, they can grow large enough to cause discomfort or be bothersome.
9. Mucous Cyst
Mucous cysts are small, fluid-filled lumps that form near the lips or inside the mouth when salivary glands become blocked. They are often caused by trauma to the area, such as biting the lip, or poor dental hygiene. Mucous cysts usually go away on their own but may require medical attention if they recur frequently.
10. Branchial Cleft Cyst
A branchial cleft cyst is a developmental abnormality that results in a lump forming near the neck or collarbone. This condition occurs during embryonic development and is typically not dangerous. However, it may cause irritation, infection, or, in rare cases, complications.
11. Perineural (Tarlov) Cyst
A perineural cyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops on the spine. Though its exact cause is unknown, these cysts can be linked to back trauma or injury. While they may cause pain in the lower back or legs in some individuals, they often go unnoticed unless they become large enough to press on surrounding nerves.
Pseudocysts
A pseudocyst resembles a cyst, but it lacks the lining that is typically found in a true cyst. Pseudocysts can form due to certain infections, trauma, or other health conditions. Some common types of pseudocysts include:
- Folliculitis (Ingrown Hair Cyst): Often the result of a fungal or bacterial infection, folliculitis occurs when hair follicles become inflamed, leading to small, pimple-like bumps. These cysts can be seen in individuals who shave or wax regularly.
- Razor Bumps (Pseudofolliculitis Barbae): Razor bumps are similar to folliculitis but are typically caused by hair growing back into the skin after shaving or waxing.
Causes of Cysts
Cysts can develop for various reasons, including:
- Blockage of Ducts or Hair Follicles: This is one of the most common causes of cysts, as seen with epidermoid and sebaceous cysts.
- Infections: Some cysts, like mucous cysts or folliculitis, occur as a result of infections.
- Injury or Trauma: Ganglion cysts and perineural cysts may form after an injury or excessive stress on a joint or nerve.
- Genetic Factors: Certain conditions, like Gardner syndrome, can cause an individual to develop multiple cysts.
When to Seek Help
Most cysts are harmless and don’t require immediate treatment. However, if you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional:
- Sudden growth or change in appearance of a cyst
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling
- Discharge of fluid or pus
- Inflammation or redness around the cyst
- Difficulty moving the affected area
Treatment Options for Cysts
Treatment for cysts depends on their type, size, and location. Common treatment options include:
- Observation: In many cases, cysts can be monitored over time to see if they cause any issues.
- Drainage: Some cysts can be drained to relieve symptoms and reduce swelling.
- Surgical Removal: In cases where a cyst is large, infected, or causing significant discomfort, surgical removal may be necessary.
Prevention of Cysts
While it’s not always possible to prevent cysts, maintaining good hygiene, avoiding excessive pressure or friction on skin, and treating underlying conditions can help reduce the risk of cyst formation. Additionally, addressing any medical issues such as infections or hormonal imbalances can help prevent certain types of cysts from developing.
Outlook
Most cysts are benign and do not cause serious health problems. However, if a cyst becomes infected or grows large, it may cause pain or complications. With appropriate treatment, most cysts can be successfully managed. If you have concerns about a cyst or notice any changes in its size or appearance, it’s important to seek medical advice.



